中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 273-282.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00021
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-11-21
修回日期:2024-02-18
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2024-03-19
通讯作者:
杨红玲,李玉霖
作者简介:杨红玲(E-mail: yanghl@lzb.ac.cn)基金资助:
Li Cheng1,2( ), Zhiying Ning1, Hongling Yang1(
), Zhiying Ning1, Hongling Yang1( ), Yulin Li1(
), Yulin Li1( )
)
Received:2023-11-21
Revised:2024-02-18
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2024-03-19
Contact:
Hongling Yang,Yulin Li
摘要:
沙漠化是科尔沁沙地土地退化的主要原因,科学合理的治沙措施能够有效控制风沙侵害,有助于植被-土壤系统的重建与恢复。本研究以科尔沁沙地高大流动沙丘和平缓流动沙丘为研究对象,通过分析自然恢复、种植差不嘎蒿(Artemisia halodendron)和设置草方格沙障3种固沙措施下植被群落特性和土壤理化性质的变化趋势,从而为该类型沙丘固沙措施的筛选提供科学指导。结果表明:(1)不同固沙措施下平缓流动沙丘植物物种丰富度为设置草方格沙障(20种)>种植差不嘎蒿(18种)>自然恢复(15种);高大流动沙丘植物物种丰富度为设置草方格沙障(14种)>种植差不嘎蒿(8种)>自然恢复(5种)。(2)高大和平缓流动沙丘土壤理化性质差异不显著;设置草方格沙障显著增加土壤有机碳、全氮含量(P<0.05);随着恢复年限延长,土壤养分含量显著增加(P<0.05)。(3)高大和平缓流动沙丘中土壤有机碳含量、全氮含量与物种丰富度呈显著正相关关系(P<0.05)。综上所述,草方格沙障能够显著改善植物群落物种丰富度,增加土壤养分以改善土壤质量,是最有利于科尔沁沙地流动沙丘生态系统恢复的措施。生态恢复是一个相对漫长的过程,随着固沙年限增加,自然恢复、种植差不嘎蒿和设置草方格沙障均有利于科尔沁沙地流动沙丘的生态恢复。
中图分类号:
程莉, 宁志英, 杨红玲, 李玉霖. 固沙措施对流动沙丘植被和土壤特性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 273-282.
Li Cheng, Zhiying Ning, Hongling Yang, Yulin Li. Effects of different sand-fixation measures on vegetation and soil characteristics of high and flat mobile dunes[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 273-282.
| 物种 | 重要值 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然恢复 | 种植差不嘎蒿 | 设置草方格沙障 | |||||||
| 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | |
| 蒺藜 | 0.010 | ||||||||
| 大果虫实 | 0.008 | 0.038 | 0.016 | 0.028 | |||||
| 地锦 | 0.021 | 0.007 | |||||||
| 锋芒草 | 0.015 | ||||||||
| 狗尾草 | 0.058 | 0.046 | 0.097 | 0.072 | 0.048 | 0.025 | 0.070 | 0.054 | 0.370 |
| 画眉草 | 0.014 | 0.030 | 0.014 | 0.028 | |||||
| 苦荬菜 | 0.013 | ||||||||
| 毛马唐 | 0.059 | 0.009 | 0.065 | 0.059 | 0.053 | ||||
| 沙蓬 | 0.942 | 0.763 | 0.807 | 0.351 | 0.447 | 0.223 | 0.792 | 0.706 | 0.443 |
| 砂蓝刺头 | 0.008 | ||||||||
| 雾滨藜 | 0.020 | 0.047 | |||||||
| 猪毛菜 | 0.006 | 0.060 | 0.014 | ||||||
| 猪毛蒿 | 0.017 | ||||||||
| 一年生植物 | 1 | 0.808 | 0.984 | 0.438 | 0.535 | 0.263 | 1 | 1 | 0.947 |
| 白草 | 0.035 | ||||||||
| 扁蓿豆 | 0.003 | ||||||||
| 差不嘎蒿 | 0.192 | 0.016 | 0.514 | 0.465 | 0.737 | 0.009 | |||
| 达乌里胡枝子 | 0.048 | 0.115 | |||||||
| 多年生植物 | 0 | 0.192 | 0.016 | 0.562 | 0.465 | 0.737 | 0 | 0 | 0.163 |
| 物种丰富度 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 12 |
表1 高大流动沙丘不同固沙措施样地中植物物种重要值变化
Table 1 Changes of important values of plant species in the high mobile dunes with different sand fixation measures
| 物种 | 重要值 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然恢复 | 种植差不嘎蒿 | 设置草方格沙障 | |||||||
| 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | |
| 蒺藜 | 0.010 | ||||||||
| 大果虫实 | 0.008 | 0.038 | 0.016 | 0.028 | |||||
| 地锦 | 0.021 | 0.007 | |||||||
| 锋芒草 | 0.015 | ||||||||
| 狗尾草 | 0.058 | 0.046 | 0.097 | 0.072 | 0.048 | 0.025 | 0.070 | 0.054 | 0.370 |
| 画眉草 | 0.014 | 0.030 | 0.014 | 0.028 | |||||
| 苦荬菜 | 0.013 | ||||||||
| 毛马唐 | 0.059 | 0.009 | 0.065 | 0.059 | 0.053 | ||||
| 沙蓬 | 0.942 | 0.763 | 0.807 | 0.351 | 0.447 | 0.223 | 0.792 | 0.706 | 0.443 |
| 砂蓝刺头 | 0.008 | ||||||||
| 雾滨藜 | 0.020 | 0.047 | |||||||
| 猪毛菜 | 0.006 | 0.060 | 0.014 | ||||||
| 猪毛蒿 | 0.017 | ||||||||
| 一年生植物 | 1 | 0.808 | 0.984 | 0.438 | 0.535 | 0.263 | 1 | 1 | 0.947 |
| 白草 | 0.035 | ||||||||
| 扁蓿豆 | 0.003 | ||||||||
| 差不嘎蒿 | 0.192 | 0.016 | 0.514 | 0.465 | 0.737 | 0.009 | |||
| 达乌里胡枝子 | 0.048 | 0.115 | |||||||
| 多年生植物 | 0 | 0.192 | 0.016 | 0.562 | 0.465 | 0.737 | 0 | 0 | 0.163 |
| 物种丰富度 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 12 |
| 物种 | 重要值 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然恢复 | 种植差不嘎蒿 | 设置草方格沙障 | |||||||
| 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | |
| 苍耳 | 0.013 | ||||||||
| 刺蒺 | 0.006 | 0.006 | |||||||
| 大果虫实 | 0.043 | 0.007 | 0.015 | 0.019 | 0.017 | 0.038 | 0.055 | 0.019 | 0.031 |
| 地锦 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.011 | 0.006 | |||||
| 狗尾草 | 0.176 | 0.108 | 0.204 | 0.129 | 0.096 | 0.189 | 0.232 | 0.127 | 0.381 |
| 画眉草 | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.002 | 0.036 | 0.018 | 0.012 | |||
| 尖头叶藜 | 0.052 | ||||||||
| 苦荬菜 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.008 | ||||||
| 牻牛儿苗 | 0.003 | ||||||||
| 毛马唐 | 0.020 | 0.021 | 0.044 | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.061 | 0.093 | 0.094 | 0.063 |
| 三芒草 | 0.005 | 0.047 | |||||||
| 沙地旋覆花 | 0.215 | 0.361 | 0.277 | 0.161 | 0.053 | ||||
| 沙蓬 | 0.496 | 0.448 | 0.290 | 0.439 | 0.584 | 0.450 | 0.347 | 0.567 | 0.105 |
| 砂蓝刺头 | 0.002 | 0.025 | 0.014 | ||||||
| 菟丝子 | 0.009 | ||||||||
| 雾滨藜 | 0.078 | 0.033 | 0.025 | 0.055 | 0.143 | ||||
| 野菽 | 0.006 | ||||||||
| 猪毛菜 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.042 | 0.004 | 0.024 | 0.004 | |||
| 猪毛蒿 | 0.001 | 0.031 | 0.015 | ||||||
| 一年生植物 | 0.954 | 0.968 | 0.944 | 0.621 | 0.845 | 0.823 | 0.996 | 0.977 | 0.806 |
| 扁蓿豆 | 0.017 | ||||||||
| 差不嘎蒿 | 0.020 | 0.343 | 0.151 | 0.142 | 0.012 | 0.036 | |||
| 达乌里胡枝子 | 0.024 | 0.006 | 0.176 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.122 | |||
| 赖草 | 0.087 | ||||||||
| 芦苇 | 0.046 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.018 | 0.014 | ||||
| 小叶锦鸡儿 | 0.003 | 0.011 | |||||||
| 直立黄芪 | 0.004 | 0.020 | |||||||
| 多年生植物 | 0.046 | 0.032 | 0.056 | 0.385 | 0.157 | 0.342 | 0.016 | 0.032 | 0.282 |
| 物种丰富度 | 7 | 10 | 12 | 7 | 12 | 16 | 10 | 14 | 15 |
表2 平缓流动沙丘不同固沙措施样地中植物物种重要值变化
Table 2 Changes of important values of plant species in the flat mobile dunes with different sand fixation measures
| 物种 | 重要值 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然恢复 | 种植差不嘎蒿 | 设置草方格沙障 | |||||||
| 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | |
| 苍耳 | 0.013 | ||||||||
| 刺蒺 | 0.006 | 0.006 | |||||||
| 大果虫实 | 0.043 | 0.007 | 0.015 | 0.019 | 0.017 | 0.038 | 0.055 | 0.019 | 0.031 |
| 地锦 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.011 | 0.006 | |||||
| 狗尾草 | 0.176 | 0.108 | 0.204 | 0.129 | 0.096 | 0.189 | 0.232 | 0.127 | 0.381 |
| 画眉草 | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.002 | 0.036 | 0.018 | 0.012 | |||
| 尖头叶藜 | 0.052 | ||||||||
| 苦荬菜 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.008 | ||||||
| 牻牛儿苗 | 0.003 | ||||||||
| 毛马唐 | 0.020 | 0.021 | 0.044 | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.061 | 0.093 | 0.094 | 0.063 |
| 三芒草 | 0.005 | 0.047 | |||||||
| 沙地旋覆花 | 0.215 | 0.361 | 0.277 | 0.161 | 0.053 | ||||
| 沙蓬 | 0.496 | 0.448 | 0.290 | 0.439 | 0.584 | 0.450 | 0.347 | 0.567 | 0.105 |
| 砂蓝刺头 | 0.002 | 0.025 | 0.014 | ||||||
| 菟丝子 | 0.009 | ||||||||
| 雾滨藜 | 0.078 | 0.033 | 0.025 | 0.055 | 0.143 | ||||
| 野菽 | 0.006 | ||||||||
| 猪毛菜 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.042 | 0.004 | 0.024 | 0.004 | |||
| 猪毛蒿 | 0.001 | 0.031 | 0.015 | ||||||
| 一年生植物 | 0.954 | 0.968 | 0.944 | 0.621 | 0.845 | 0.823 | 0.996 | 0.977 | 0.806 |
| 扁蓿豆 | 0.017 | ||||||||
| 差不嘎蒿 | 0.020 | 0.343 | 0.151 | 0.142 | 0.012 | 0.036 | |||
| 达乌里胡枝子 | 0.024 | 0.006 | 0.176 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.122 | |||
| 赖草 | 0.087 | ||||||||
| 芦苇 | 0.046 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.018 | 0.014 | ||||
| 小叶锦鸡儿 | 0.003 | 0.011 | |||||||
| 直立黄芪 | 0.004 | 0.020 | |||||||
| 多年生植物 | 0.046 | 0.032 | 0.056 | 0.385 | 0.157 | 0.342 | 0.016 | 0.032 | 0.282 |
| 物种丰富度 | 7 | 10 | 12 | 7 | 12 | 16 | 10 | 14 | 15 |
| 项目 | 物种丰富度 | 植被盖度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | |
| 沙丘类型 | 48.25 | < 0.001 | 4.926 | 0.029 |
| 固沙措施 | 12.93 | < 0.001 | 2.601 | 0.080 |
| 年份 | 7.544 | 0.001 | 11.80 | < 0.001 |
| 沙丘类型×固沙措施 | 1.010 | 0.406 | 0.525 | 0.717 |
| 沙丘类型×年份 | 0.573 | 0.566 | 8.081 | 0.001 |
| 固沙措施×年份 | 0.622 | 0.648 | 0.935 | 0.448 |
| 沙丘类型×固沙措施×年份 | 2.745 | 0.070 | 0.073 | 0.930 |
表3 高大和平缓流动沙丘不同固沙措施对植被群落特征影响的方差分析
Table 3 ANOVA analysis of different sand fixation measures on vegetation community characteristics in high and flat mobile sand dunes
| 项目 | 物种丰富度 | 植被盖度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | |
| 沙丘类型 | 48.25 | < 0.001 | 4.926 | 0.029 |
| 固沙措施 | 12.93 | < 0.001 | 2.601 | 0.080 |
| 年份 | 7.544 | 0.001 | 11.80 | < 0.001 |
| 沙丘类型×固沙措施 | 1.010 | 0.406 | 0.525 | 0.717 |
| 沙丘类型×年份 | 0.573 | 0.566 | 8.081 | 0.001 |
| 固沙措施×年份 | 0.622 | 0.648 | 0.935 | 0.448 |
| 沙丘类型×固沙措施×年份 | 2.745 | 0.070 | 0.073 | 0.930 |
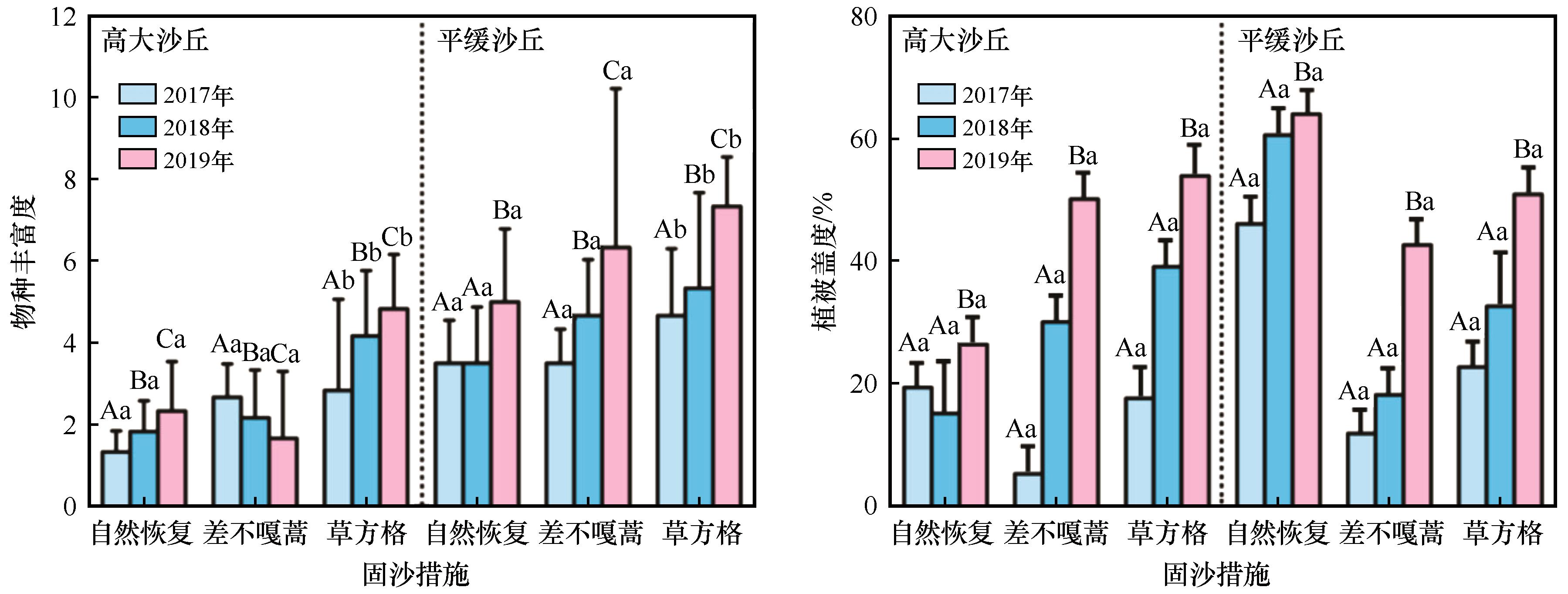
图1 固沙措施对沙丘植被群落特征的影响。注:不同大写字母代表年份之间差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母代表固沙措施之间差异显著(P <0.05)
Fig.1 Effects of sand fixation measures on vegetation community characteristics of mobile dunes
| 项目 | 土壤含水量 | 土壤有机碳含量 | 土壤全氮含量 | 砂粒 | 粉粒 | 黏粒 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 沙丘类型 | 0.004 | 0.950 | 1.008 | 0.318 | 1.514 | 0.222 | 0.025 | 0.874 | 1.852 | 0.177 | 2.048 | 0.156 |
| 固沙措施 | 4.537 | 0.013 | 70.334 | < 0.001 | 45.542 | < 0.001 | 8.353 | < 0.001 | 1.487 | 0.232 | 7.154 | 0.001 |
| 年份 | 68.079 | < 0.001 | 7.797 | 0.001 | 5.165 | 0.008 | 0.253 | 0.777 | 1.287 | 0.281 | 1.444 | 0.241 |
| 沙丘类型×固沙措施 | 0.255 | 0.960 | 0.822 | 0.514 | 0.349 | 0.844 | 0.982 | 0.422 | 0.323 | 0.862 | 1.246 | 0.297 |
| 沙丘类型×年份 | 0.566 | 0.570 | 0.001 | 1.000 | 0.052 | 0.949 | 2.025 | 0.138 | 4.059 | 0.060 | 4.088 | 0.060 |
| 固沙措施×年份 | 1.029 | 0.397 | 0.378 | 0.824 | 1.471 | 0.217 | 0.191 | 0.943 | 0.067 | 0.992 | 0.222 | 0.926 |
| 沙丘类型×固沙措施×年份 | 0.432 | 0.651 | 1.086 | 0.342 | 0.574 | 0.566 | 0.082 | 0.921 | 0.130 | 0.879 | 0.347 | 0.708 |
表4 高大和平缓流动沙丘固沙措施对土壤性质影响的方差分析
Table 4 ANOVA analysis of different sand fixation measures on soil properties in high and flat mobile sand dunes
| 项目 | 土壤含水量 | 土壤有机碳含量 | 土壤全氮含量 | 砂粒 | 粉粒 | 黏粒 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 沙丘类型 | 0.004 | 0.950 | 1.008 | 0.318 | 1.514 | 0.222 | 0.025 | 0.874 | 1.852 | 0.177 | 2.048 | 0.156 |
| 固沙措施 | 4.537 | 0.013 | 70.334 | < 0.001 | 45.542 | < 0.001 | 8.353 | < 0.001 | 1.487 | 0.232 | 7.154 | 0.001 |
| 年份 | 68.079 | < 0.001 | 7.797 | 0.001 | 5.165 | 0.008 | 0.253 | 0.777 | 1.287 | 0.281 | 1.444 | 0.241 |
| 沙丘类型×固沙措施 | 0.255 | 0.960 | 0.822 | 0.514 | 0.349 | 0.844 | 0.982 | 0.422 | 0.323 | 0.862 | 1.246 | 0.297 |
| 沙丘类型×年份 | 0.566 | 0.570 | 0.001 | 1.000 | 0.052 | 0.949 | 2.025 | 0.138 | 4.059 | 0.060 | 4.088 | 0.060 |
| 固沙措施×年份 | 1.029 | 0.397 | 0.378 | 0.824 | 1.471 | 0.217 | 0.191 | 0.943 | 0.067 | 0.992 | 0.222 | 0.926 |
| 沙丘类型×固沙措施×年份 | 0.432 | 0.651 | 1.086 | 0.342 | 0.574 | 0.566 | 0.082 | 0.921 | 0.130 | 0.879 | 0.347 | 0.708 |
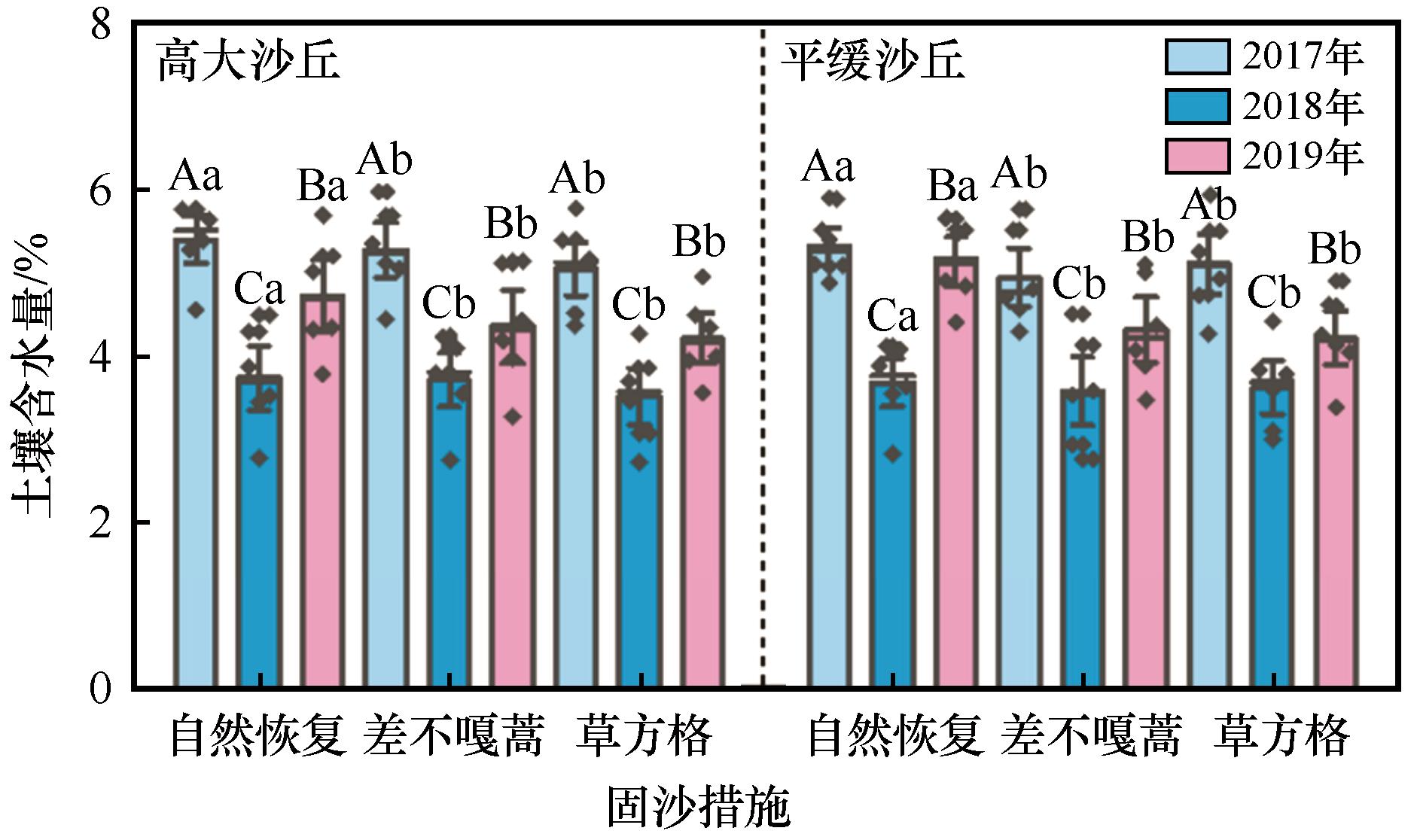
图2 固沙措施对沙丘植被恢复过程中土壤含水量的影响注:不同大写字母代表年份之间差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母代表固沙措施之间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.2 Effects of different sand fixation measures on soil water content in high and flat mobile dunes
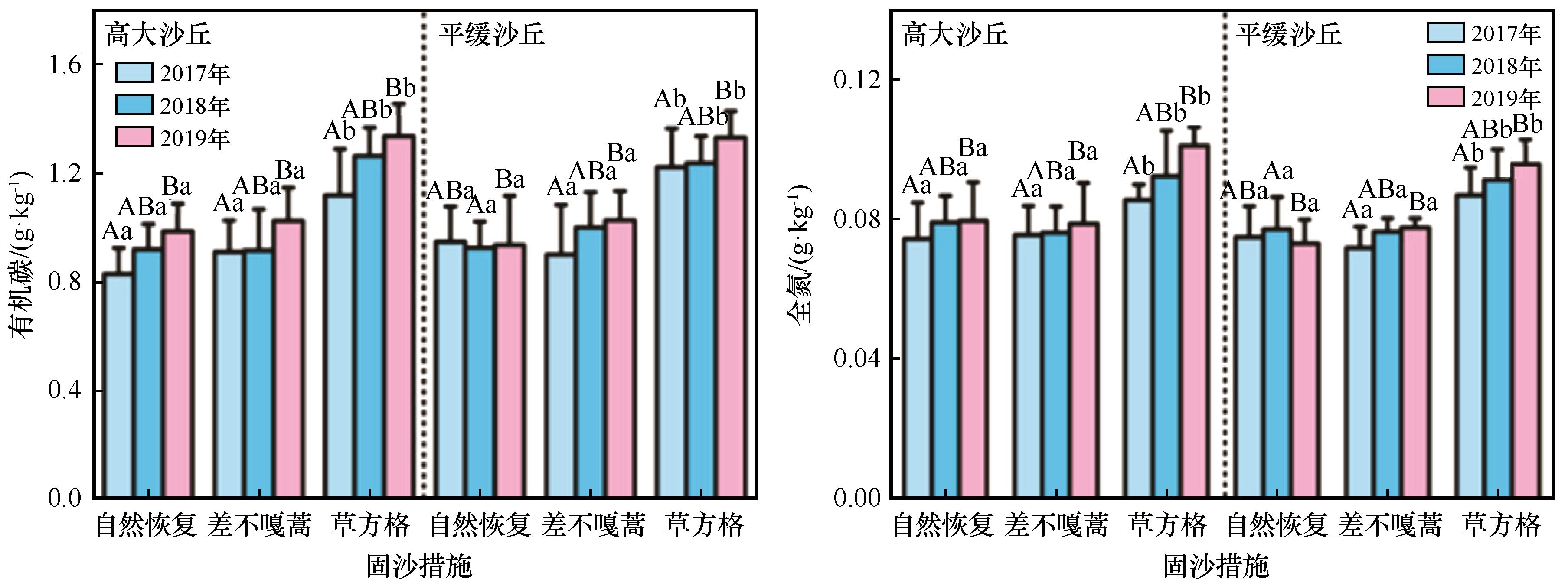
图3 固沙措施对沙丘恢复过程中土壤化学性质的影响注:不同大写字母代表年份之间差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母代表固沙措施之间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.3 Effects of different sand fixation measures on soil chemical properties in high and flat mobile dunes
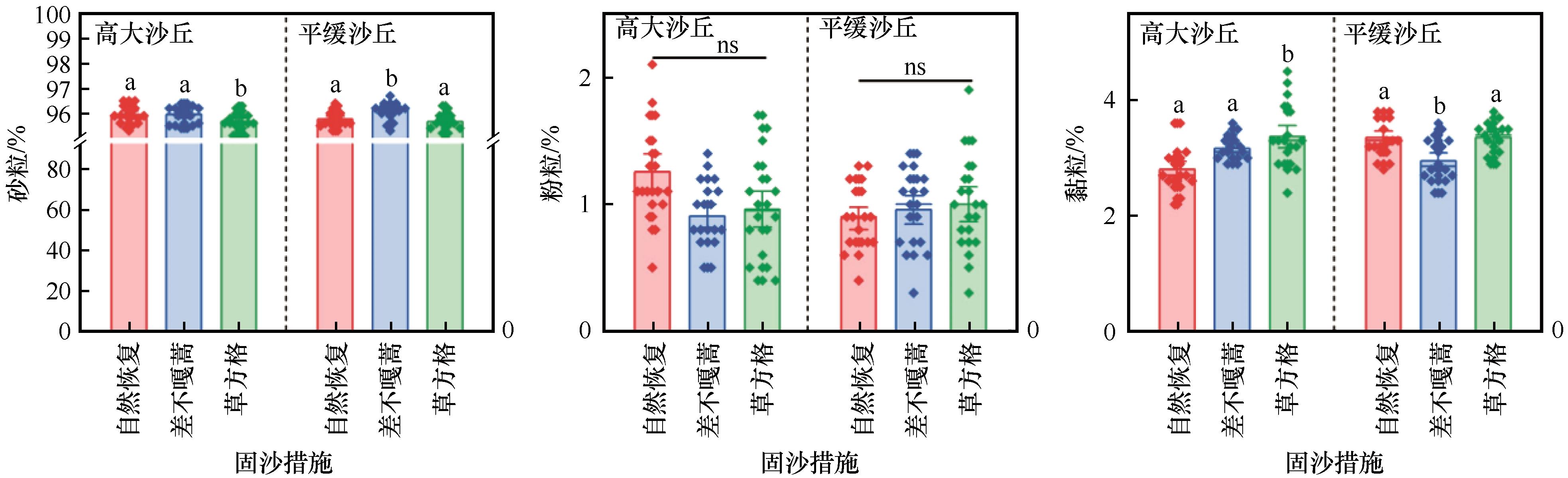
图4 固沙措施对沙丘土壤机械组成的影响注:不同小写字母代表固沙措施之间差异显著(P<0.05),ns表示无显著差异(P>0.05)
Fig.4 Effects of different sand fixation measures on soil texture in high and flat mobile dunes
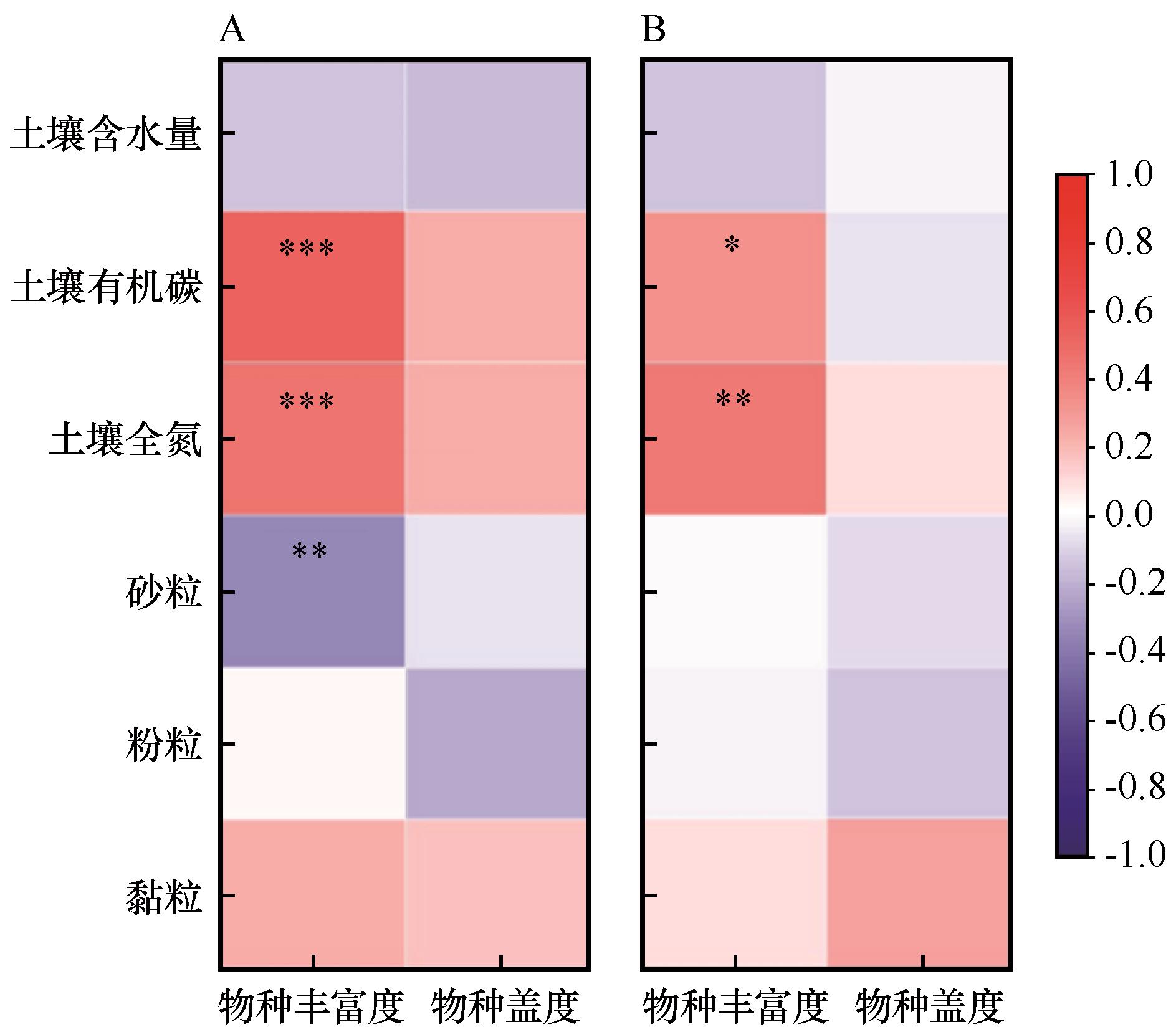
图5 高大(A)和平缓(B)流动沙丘土壤理化性质与植被群落特征相关性分析注:*,在0.05水平上显著相关;**, 在0.01水平上显著相关;***,在0.001水平上显著相关
Fig.5 Correlations between soil properties and vegetation characteristics of high (A) and flat (B) mobile dunes
| 1 | 欧阳志云,崔书红,郑华.我国生态安全面临的挑战与对策[J].科学与社会,2015,5(1):20-30. |
| 2 | 赵其国,黄国勤,马艳芹.中国生态环境状况与生态文明建设[J].生态学报,2016,36(19):6328-6335. |
| 3 | 傅伯杰.国土空间生态修复亟待把握的几个要点[J].中国科学院院刊,2021,36(1):64-69. |
| 4 | 昝国盛,王翠萍,李锋,等.第六次全国荒漠化和沙化调查主要结果及分析[J].林业资源管理,2023(1):1-7. |
| 5 | 张凤荣,周建,徐艳,等.基于地学规律的科尔沁沙地土地整治与生态修复规划方法[J].地学前缘,2021,28(4):35-41. |
| 6 | 刘帅飞,曲海华,高广磊,等.中国履行《联合国防治荒漠化公约》:行动、问题与对策[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(6):229-236. |
| 7 | 王涛 朱震达.我国沙漠化研究的若干问题:1.沙漠化的概念及其内涵[J].中国沙漠,2003,23(3):3-8. |
| 8 | 李新荣.干旱沙区土壤空间异质性变化对植被恢复的影响[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学),2005(4):361-370. |
| 9 | 于凤龙,谭瑞虹,李成喜.生物沙障治沙造林技术研究[J].农业与技术,2013,33(6):47-48. |
| 10 | 苗仁辉,郭美霞,刘银占.不同生物沙障对科尔沁流动沙丘植被恢复及土壤湿度的影响[J].生态环境学报,2018,27(11):1987-1992. |
| 11 | 张文军,刘德义,李泽江,等.科尔沁沙地植物再生沙障人工群落结构特征[J].中国水土保持科学,2007(5):56-99. |
| 12 | 胡小龙,薛博,刘莉莉,等.科尔沁沙地杨柴生物沙障平茬复壮技术研究[J].内蒙古林业科技,2011,37(4):8-12. |
| 13 | 李爽,纪晓林,黄选瑞,等.冀北沙漠化土地黄柳生物沙障防风阻沙与土壤改良效益分析[J].河北农业大学学报,2010,33(1):12-16. |
| 14 | 曹银贵,荆炎幸.自然恢复的认知体系[J].中国土地,2023 (12):29-31. |
| 15 | 邓汉文.长期围封对退化草原植被、土壤理化及土壤微生物特征的影响[D].山东烟台:鲁东大学,2021. |
| 16 | 李佳秀,张青松,吴勇,等.围封对草地植被生长和土壤特性的影响研究进展[J].中国草地学报,2023,45(5):137-150. |
| 17 | 李玉霖,孟庆涛,赵学勇,等.科尔沁沙地流动沙丘植被恢复过程中群落组成及植物多样性演变特征[J].草业学报,2007(6):54-61. |
| 18 | 王旭洋,李玉强,罗永清,等.科尔沁沙地不同生境植被凋落物年际及年内动态[J].应用生态学报,2018,29(5):1494-1502. |
| 19 | 吴丹丹,蔡运龙.中国生态恢复效果评价研究综述[J].地理科学进展,2009,28(4):622-628. |
| 20 | 李玉强,赵哈林,赵学勇,等.科尔沁沙地沙漠化过程中土壤碳氮特征分析[J].水土保持学报,2005(5):75-78. |
| 21 | 杨红玲,李玉霖,宁志英,等.添加混合凋落物对沙丘草地土壤有机碳矿化的影响[J].生态学报,2019,39(7):2510-2519. |
| 22 | Fan S Y, Zhou L H.Desertification control in China:possible solutions[J].Ambio,2001,30(6):384-385. |
| 23 | 苏永中,赵哈林,张铜会,等.科尔沁沙地不同年代小叶锦鸡儿人工林植物群落特征及其土壤特性[J].植物生态学报,2004(1):93-100. |
| 24 | 王新源,马立鹏,程小云,等.不同治沙措施对荒漠绿洲过渡带植物群落与土壤因子的影响[J].生态学报,2022,42(14):5869-5883. |
| 25 | 王新源,兰芳芳,马仲武,等.治沙措施通过植物群落的质量效应驱动土壤因子变化:以玛曲高寒草甸沙化区为例[J].生态学报,2023,43(1):70-81. |
| 26 | Zuo X A, Zhao X Y, Zhao H L,et al.Spatial heterogeneity of soil properties and vegetation-soil relationships following vegetation restoration of mobile dunes in Horqin Sandy Land,Northern China[J].Plant and Soil,2009,318(1):153-167. |
| 27 | Miao R, Jiang D, Musa A,et al.Effectiveness of shrub planting and grazing exclusion on degraded sandy grassland restoration in Horqin sandy land in Inner Mongolia[J].Ecological Engineering,2015,74:164-173. |
| 28 | Zhu G Y, Deng L, Zhang X B,et al.Effects of grazing exclusion on plant community and soil physicochemical properties in a desert steppe on the Loess Plateau,China[J].Ecological Engineering,2016,90:372-381. |
| 29 | Dai L, Guo X, Ke X,et al.Moderate grazing promotes the root biomass in Kobresia meadow on the northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J].Ecology and Evolution,2019,9(16):9395-9406. |
| 30 | Hu Y F, Shu X Y, He J,et al.Storage of C,N,and P affected by afforestation with Salix cupularis in an alpine semiarid desert ecosystem[J].Land Degradation & Development,2018,29(1):188-198. |
| 31 | Li X R, Xiao H L, He M Z,et al.Sand barriers of straw checkerboards for habitat restoration in extremely arid desert regions[J].Ecological Engineering,2006,28(2):149-157. |
| 32 | 许永利,马树彪,马文喜.沙柳沙障对土壤水分和养分的影响[J].安徽农业科学,2013,41(33):12866-12869. |
| 33 | 高菲,高永,高强,等.沙柳沙障对土壤理化性质的影响[J].内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版),2006(2):39-42. |
| 34 | 黄巍,杨涛,石长春.设置沙柳沙障对沙丘土壤理化性质的影响[J].防护林科技,2014(8):5-7. |
| 35 | 王丽英,李红丽,董智,等.沙柳沙障对沙丘沙粒度组成与特征的影响[J].中国水土保持科学,2013,11(4):53-59. |
| 36 | 张婷,翁月,姚凤娇,等.放牧强度对草甸植物小叶章及土壤化学计量比的影响[J].草业学报,2014,23(2):20-28. |
| 37 | 许雪贇,曹建军,杨淋,等.放牧与围封对青藏高原草地土壤和植物叶片化学计量学特征的影响[J].生态学杂志,2018,37(5):1349-1355. |
| 38 | 王国华,任亦君,缑倩倩.河西走廊荒漠绿洲过渡带封育对土壤和植被的影响[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(2):222-231. |
| 39 | Su Y Z, Wang X F, Yang R,et al.Effects of sandy desertified land rehabilitation on soil carbon sequestration and aggregation in an arid region in China[J].Journal of Environment Management,2010,91(11):2109-2116. |
| 40 | 苏永中,刘婷娜.流动沙地建植人工固沙梭梭林的土壤演变过程[J].土壤学报,2020,57(1):84-91. |
| 41 | 李从娟,雷加强,高培,等.人工防护林作用下风沙土成土过程的研究进展[J].土壤学报,2012,49(6):1227-1234. |
| 42 | Hooper D U.The role of complementarity and competition in ecosystem responses to variation in plant diversity[J].Ecology,1998,79(2):704-719. |
| 43 | Wang G, Zhao W, Liu H,et al.Changes in soil and vegetation with stabilization of dunes in a desert-oasis ecotone[J].Ecological Research,2015,30(4):639-650. |
| 44 | Zhang G, Zhao L, Yang Q,et al.Effect of desert shrubs on fine-scale spatial patterns of understory vegetation in a dry-land[J].Plant Ecology,2016,217(9):1141-1155. |
| 45 | Li Y, Cui J, Zhang T,et al.Effectiveness of sand-fixing measures on desert land restoration in Kerqin Sandy Land,northern China[J].Ecological Engineering,2009,35(1):118-127. |
| 46 | Fan B, Zhang A, Yang Y,et al.Long-term effects of xerophytic Shrub Haloxylon ammodendron plantations on soil properties and vegetation dynamics in Northwest China[J].Plos One,2016,11(12). |
| 47 | Zhang G, Zhao W, Zhou H,et al.Extreme drought stress shifts net facilitation to neutral interactions between shrubs and sub-canopy plants in an arid desert[J].Oikos,2018,127(3):381-391. |
| 48 | Ffolliott P F, Gottfried G J, Rietveld W J.Dryland forestry for sustainable development[J].Journal of Arid Environments,1995,30(2):143-152. |
| [1] | 王仁德, 蒋红军, 李庆, 付刚, 李玉强, 苑依笑, 常春平, 郭中领. 土壤粉尘释放能力与土壤性质关系的初步研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 43-49. |
| [2] | 潘加朋, 张克存, 安志山, 张宏雪, 薛承杰. 风沙治理工程综合效益分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 233-242. |
| [3] | 洪光宇, 王晓江, 苏庆溥, 海龙, 王少昆, 高孝威, 徐艳艳, 周景山, 李卓凡, 李梓豪, 胡尔查. 毛乌素沙地流动沙丘土壤水分模拟及渗漏特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 288-298. |
| [4] | 陈雨晴, 席海洋, 程文举, 赵欣悦. 荒漠河岸林区3种典型植物群落下土壤碳氮含量特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 150-159. |
| [5] | 李世龙. 青藏高原东缘玛曲沙化高寒草地土壤理化性质[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 44-52. |
| [6] | 梁海荣, 王涛, 杨宇, 冯伟, 廉泓林, 刘雪锋, 李佳陶, 刘佳. 毛乌素沙地与浑善达克沙地水分深层渗漏特征对比[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 69-76. |
| [7] | 安晨宇, 王仁德, 周海涛, 李庆, 张新军, 常春平, 郭中领, 李继峰. 秋免耕对坝上地区农田风蚀及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 95-103. |
| [8] | 潘美慧, 郝泽文, 齐宇涵, 杨安娜, 陈有桂, 李晨露. 西藏朋曲流域不同地貌部位流动沙丘粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 138-147. |
| [9] | 石麟, 赵雨兴, 哈斯额尔敦null, 张萍, 许映军, 王卓然. 毛乌素沙地沙障环境下的沙丘迎风坡植被及土壤养分变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 140-146. |
| [10] | 王文帆, 刘任涛, 郭志霞, 冯永宏, 蒋嘉瑜. 腾格里沙漠东南缘固沙灌丛林土壤理化性质及分形维数[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 209-218. |
| [11] | 冯筱, 屈建军, 范庆斌, 谭立海. 鼠兔(Ochotona curzoniae)洞穴堆积体对草地沙化的影响及防治[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(3): 168-176. |
| [12] | 王宇祥, 刘廷玺, 段利民, 童新, 王冠丽, 李东方, 王海英. 基于Hydrus-1D模型的科尔沁沙地沙丘-草甸相间区土壤水分动态模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 195-205. |
| [13] | 曹静, 阿拉木萨, 张圆浩. 科尔沁沙地沙丘水分深层渗漏量和侧向运移量[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(3): 41-47. |
| [14] | 张志栋, 常春平, 郭中领, 王仁德, 邢春燕. 河北坝上农田、退耕地和天然草地土壤的可风蚀性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(1): 85-91. |
| [15] | 赖俊华, 张凯, 王维树, 王彦奎, 徐贤伦, 屈建军, 肖建华. 化学固沙材料研究进展及展望[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(4): 644-658. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
